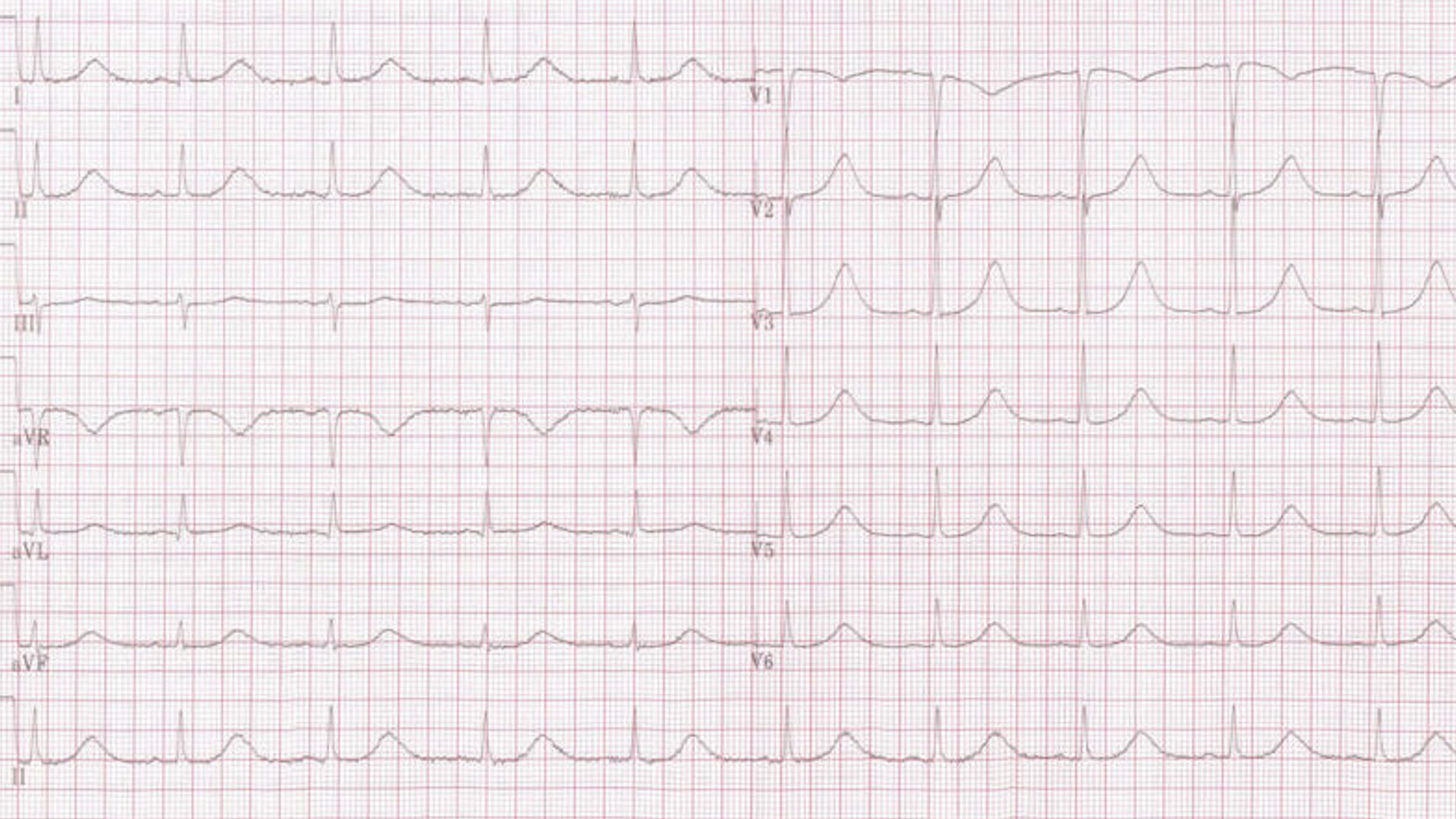
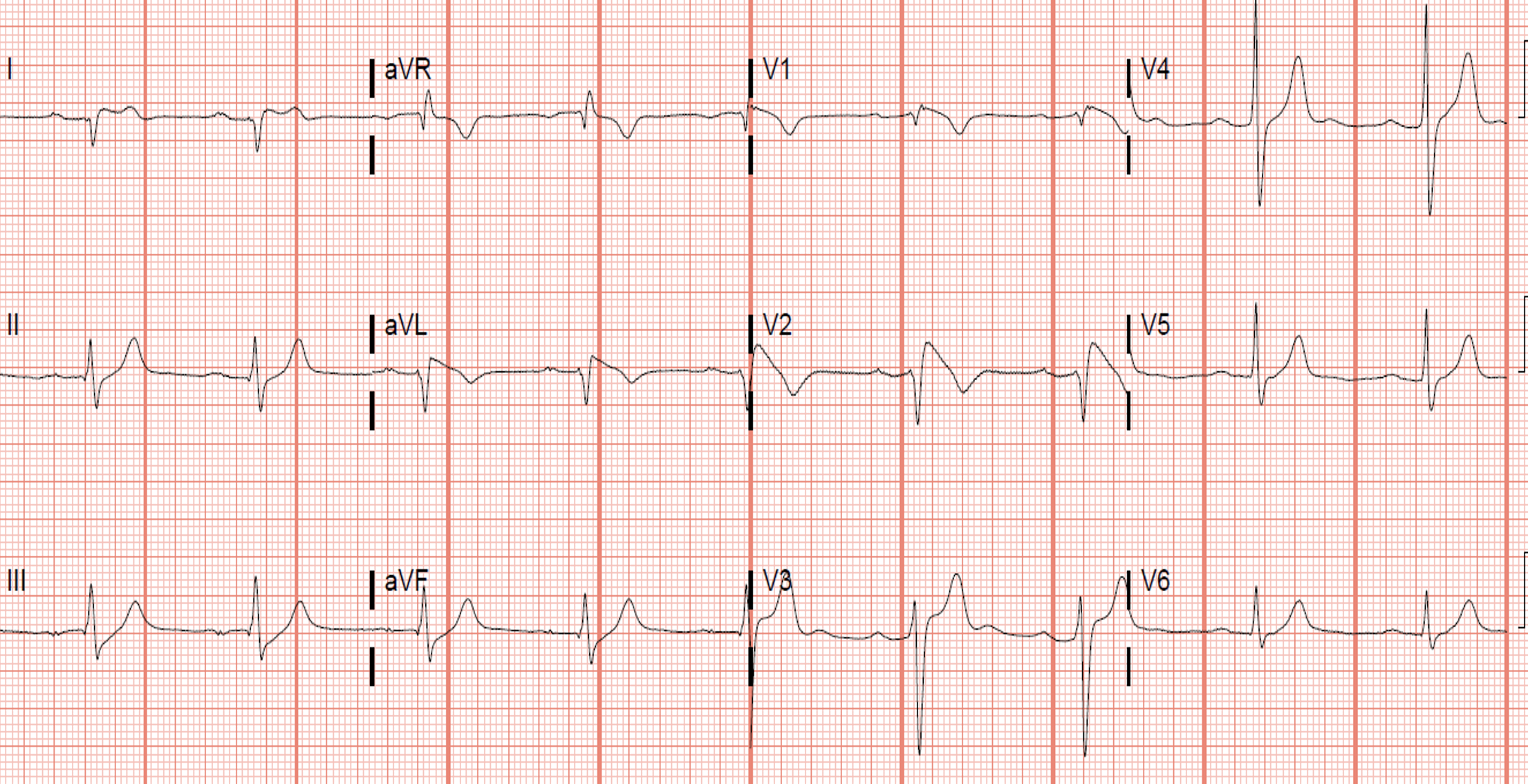
Most Patient would be asymptomatic when presented to the GP Practice. Hence ECG performed at the time would not normally demonstrate arrhythmia
Key is to identify high risk features on ECG
Younger age group with no structural abnormalities
Wolff Parkinson White syndrome
Inherited QT syndrome
Brugada
ARVC
Those with structural heart disease
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial flutter
Atrial tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia
Distinguishing these tachyarrhythmias may not necessarily be easy…
e.g. sinus vs. flutter vs. atrial tachycardia
e.g. atrial fibrillation vs. atrial tachycardia
Bradycardia
Prolonged PR (affected by Beta Blocker etc)
Bundle branch Block
Hemi Block
If there are more P wave than QRS complex and with regular RR interval- suspicious of heart blockIf there are more P wave than QRS complex and with regular RR interval- suspicious of heart block
Long QT
Brugada
Complete heart block
Dr James Fu