The cardiovascular effects of alcohol are often debated. One commonly neglected aspect is its caloric content.
Alcohol contains 7 calories per gram, compared with fat that contains 9 calories per gram and sugar that contains 4 calories per gram.
T 09-980-6363. M 022-672-8255. F 09-929-3248. consult@cardiologist.co.nz. EDI: CARDINST
North Shore - Suite 109, Level 1, 119 Apollo Drive, Albany
Silverdale - Northern Specialist Centre @Beyond; 5 Painton Road, Silverdale.
Central Auckland - 110 Specialist Centre @ Beyond;v110 Grafton Road, Grafton
East Auckland - East Care Specialist Centre, 260 Botany Road, Howick, Manukau

Elephant Hill Vineyard, Te Awanga coast, Hawkes Bay
The cardiovascular effects of alcohol are often debated. One commonly neglected aspect is its caloric content.
Alcohol contains 7 calories per gram, compared with fat that contains 9 calories per gram and sugar that contains 4 calories per gram.

Clouds above the Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Living with a heart condition can sometimes be worrying and distressing. It can take some time to adjust to what has happened. Everyone’s experience is a very personal one, and we all cope in different ways. However, sometimes individuals can feel overwhelmed and can benefit from professional help to cope and develop strategies to deal with these stresses.
Shocked… Angry… Sad… Relieved… Lucky… Worried… Frightened… loss of control… Motivated… On edge… Helpless…

The Struggle 2017; Patricia Piccinini @ Queensland Gallery of Modern Art, Aug 2018
Physical activity is one of the most important determinants of our cardiovascular risk, and not being active is responsible for more than 5 million deaths per year worldwide.
Professor Sallis from the University of California, San Diego, published an interesting article in the Lancet in 2016 outlining the importance of our neighbourhoods with different levels of walkability in influencing the amount of physical activity of the people living in those neighbourhoods.

Sea bream, white soy, pickled wakame @ Supernormal, Melbourne
Salt (sodium) intake is one of the most important causes of hypertension. Cardiologists often advise reducing salt as a way of dealing with hypertension. But where does salt in our diet usually come from?

The Midnight Baker @ Dominion Road, Mount Eden
Many believed that simply avoiding meat would constitute a healthy diet. A recent study from the Harvard School of Public health suggests otherwise. Plant-based diet must be of “high quality”, in order to reduce coronary heart disease risk.
Read more
Yum char is hugely popular in Chinese. From the heart point of view,
- multiple small plates make it quite hard to work out the right food group proportions
- many dim sums contain high overall fat content, especially saturated fat
- many dim sums contain very high salt content.
Read more
Cardiologists know of the beneficial effect of statins, the main class of medications to lower cholesterol and prevent heart attacks. Much of the evidence has been from randomized controlled trials over the last 10-20 years, where patients treated with statins were less likely to have a heart attack compared with those who were not.

After a heart attack, many patients ask their cardiologists what foods to avoid. However, one may not realize that food avoidance is not what cardiologists preach. After all, food is something we enjoy, so the focus should never be what we cannot eat, but rather how we should eat. It is about a balanced diet.
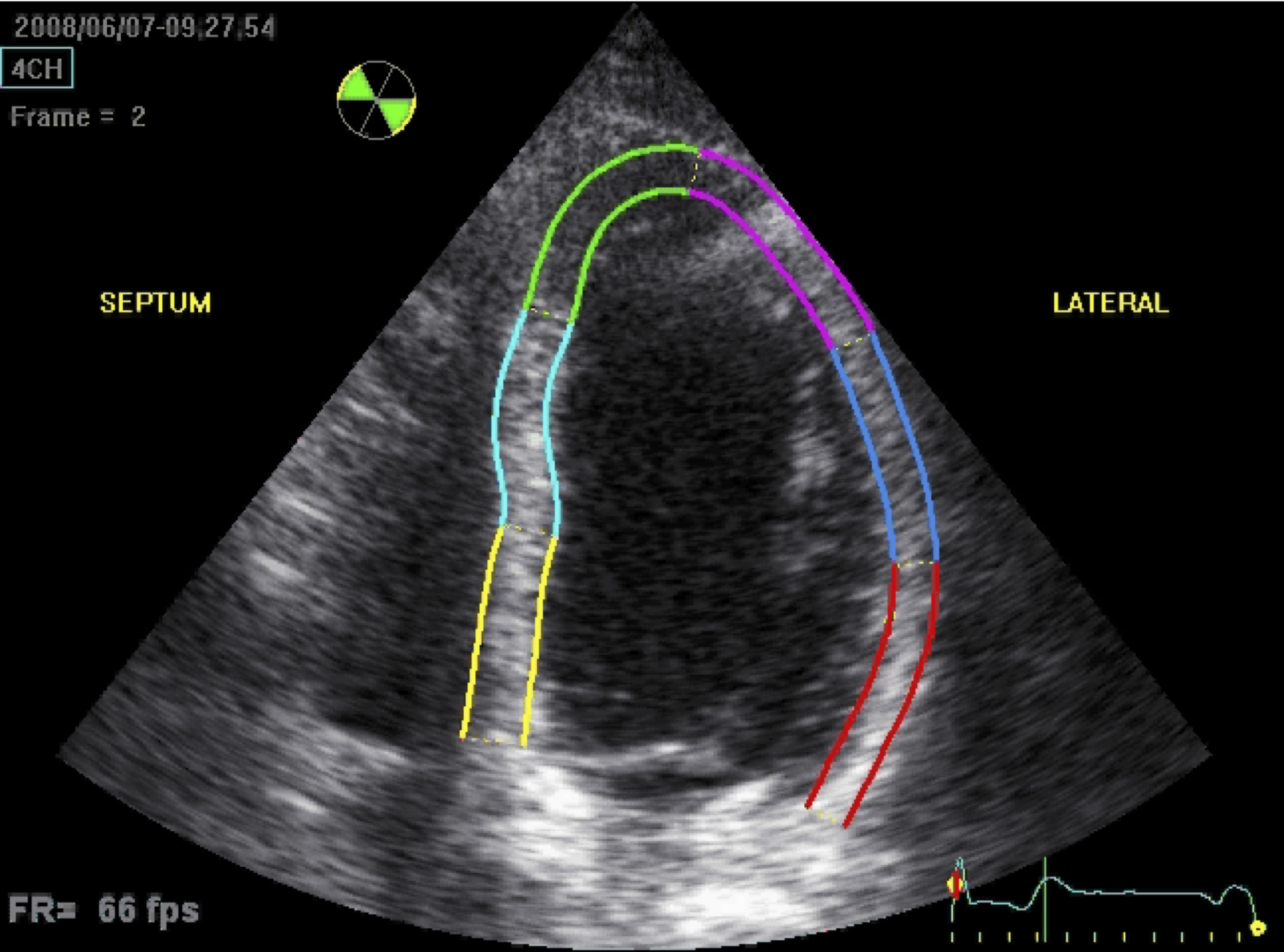
An echo image, with strain measurements, which is a novel technique looking at heart function.
Echocardiogram gives information about the heart muscle and valve functions and its one of the main tools in Cardiology. It is an ultrasound test, similar to baby ultrasound during pregnancy.
Read more
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) records the electrical activities of the heart and gives clues towards heart health.
Read moreCoronary artery disease results from the narrowing of the internal diameter of the coronary arteries. The process is called atherosclerosis. This limits the blood supply to heart, so that oxygen supply cannot match the oxygen demand of the heart.
Read more
Image courtesy of NHLBI
Atherosclerosis is the underlying cause of coronary artery disease. This results from the build up of fatty deposits inside the arterial wall over many years. Endothelial inflammation and injury, as well as the plaque buildup with lipids, macrophages, foam cells and collagen play an important part of this process.
Read more
The normal functioning of the heart muscle and valves rely on the normal functioning of the coronary arteries that provide blood supply and nutrients. The conduction system (electrical wiring system of the heart) coordinates the pumping of blood in the atria and the ventricles.
Read more